The Importance of the Carbon Cycle
The Importance of the Carbon Cycle
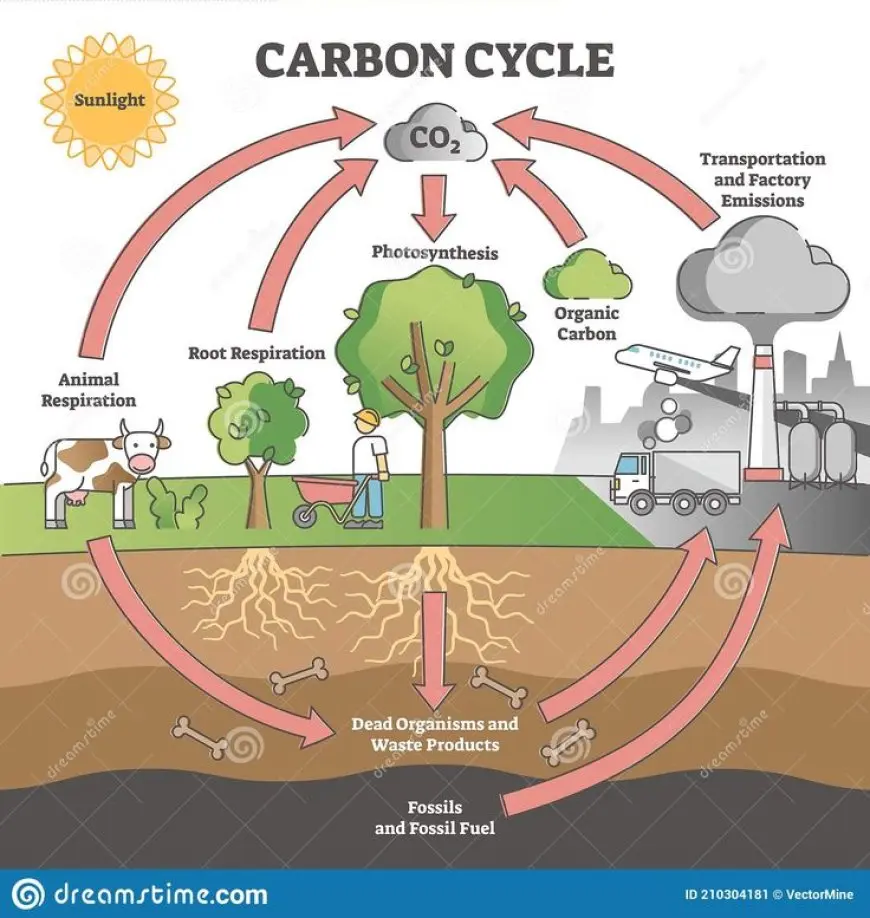
The carbon cycle is one of the most crucial processes in Earth's ecosystem, as it regulates the flow of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms. Carbon is a fundamental element that makes up all living organisms and is essential for life. The carbon cycle ensures that carbon is continually recycled, helping to maintain balance in Earth's climate, ecosystems, and biodiversity. Understanding the carbon cycle is vital for addressing climate change, as disruptions to this natural process can lead to significant environmental impacts.
What Is the Carbon Cycle?
The carbon cycle describes the continuous movement of carbon through different spheres of the Earth system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. It involves various processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion, each playing a vital role in the transformation and movement of carbon.
Carbon enters the atmosphere primarily through the process of respiration, where animals and plants release carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is also released during the burning of fossil fuels and biomass. Once in the atmosphere, carbon dioxide can be absorbed by plants during photosynthesis, where it is used to produce glucose, a sugar that plants use for energy. This carbon is then transferred to herbivores when they consume plants and to carnivores when they consume herbivores, continuing the flow of carbon through the food chain.
After plants and animals die, carbon is returned to the soil as organic matter, where it is decomposed by bacteria and fungi. Some of this carbon is stored in the soil for long periods, while the rest may be released back into the atmosphere through respiration or other processes. The ocean also plays a vital role in the carbon cycle by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in marine organisms and sediment.
The Role of the Carbon Cycle in Climate Regulation
One of the key functions of the carbon cycle is its ability to regulate Earth's climate. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, meaning it traps heat in the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect. Without the carbon cycle, the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere would be much higher, causing the Earth's climate to become significantly warmer.
However, the carbon cycle helps to maintain a balance. Plants, especially forests, act as carbon sinks by absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Oceans also store carbon and help moderate its levels. When the carbon cycle is functioning normally, these natural processes help keep Earth's temperature within a range that supports life.
Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle
In recent decades, human activities have significantly altered the carbon cycle. The burning of fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, and industrial processes have led to an increase in carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. This excess carbon dioxide has contributed to global warming and climate change. Deforestation, in particular, is a major concern, as it reduces the number of trees that can absorb carbon dioxide.
The excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is also causing ocean acidification. As the oceans absorb more carbon, the increased acidity affects marine life, particularly coral reefs and shellfish, which rely on stable conditions to thrive.
Why the Carbon Cycle Matters for Life on Earth
The carbon cycle is vital not only for maintaining climate stability but also for supporting all forms of life. Plants, which are the foundation of most food chains, rely on carbon for photosynthesis. The carbon cycle also provides the necessary conditions for soil fertility, ensuring that plants have the nutrients they need to grow. Without a stable carbon cycle, ecosystems would collapse, and life on Earth would be at risk.
Moreover, the carbon cycle helps regulate the concentration of greenhouse gases, which play a key role in maintaining Earth’s temperature. Disruptions to the carbon cycle can lead to more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and shifts in ecosystems, which affect agriculture, water resources, and biodiversity.
In summary, the carbon cycle is a fundamental process that regulates carbon flow through Earth's systems, supporting life and maintaining climate stability. Human activities have disrupted this cycle, leading to higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and contributing to climate change. Understanding and preserving the carbon cycle is crucial for mitigating the impacts of global warming and ensuring the continued health of our planet. Efforts to reduce carbon emissions, protect forests, and restore ecosystems are essential to maintaining the balance of the carbon cycle and safeguarding life on Earth.







