Why the Food Chain Is Important in Ecosystems
Why the Food Chain Is Important in Ecosystems
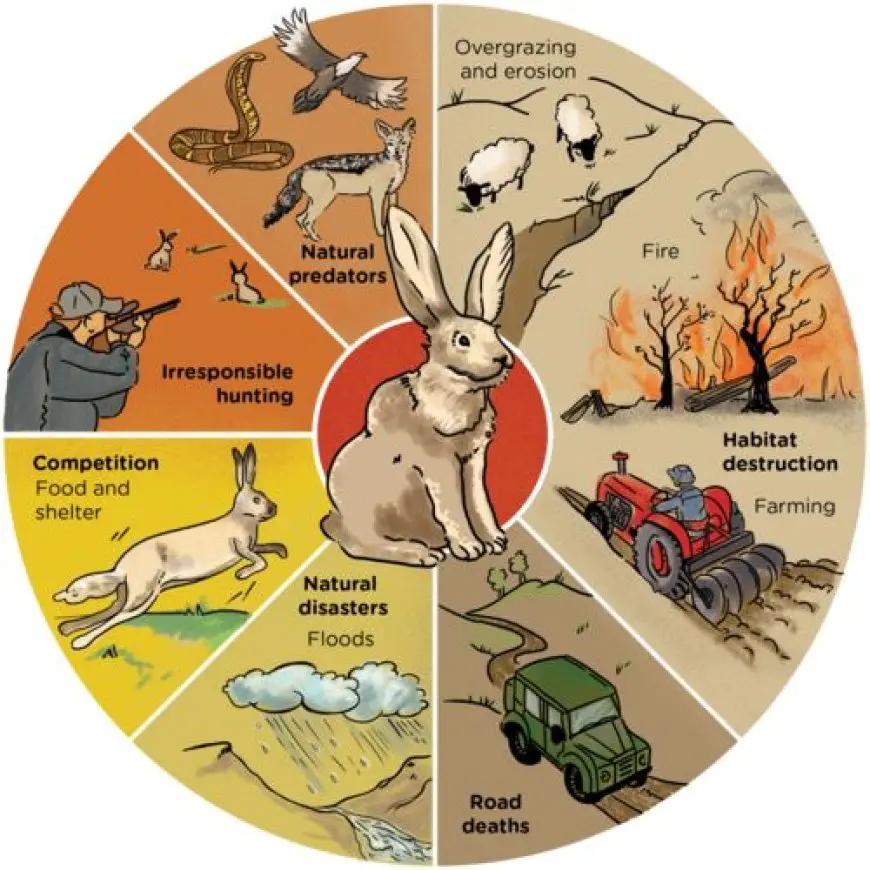
The food chain is a fundamental concept in ecology, representing the flow of energy and nutrients through different organisms in an ecosystem. It illustrates the relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers, showing how every species depends on others for survival. The importance of the food chain goes beyond simply understanding who eats whom; it highlights the delicate balance required to sustain life on Earth.
Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycling
The food chain begins with producers, such as plants and algae, which harness energy from the sun to create food through photosynthesis. This energy is passed on to primary consumers, such as herbivores, and then to secondary and tertiary consumers, including carnivores and omnivores. Finally, decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil. This continuous flow of energy and nutrients ensures the survival of all life forms and maintains the health of ecosystems.
Maintaining Balance in Ecosystems
The food chain helps maintain balance within ecosystems by regulating populations of different species. Predators control the numbers of herbivores, preventing overgrazing and the depletion of vegetation. Similarly, herbivores influence plant populations, encouraging biodiversity and preventing any single species from dominating. Disruptions in the food chain, such as the loss of a keystone species, can lead to imbalances, affecting the entire ecosystem.
Supporting Biodiversity
The interdependence shown in food chains highlights the importance of biodiversity. Each species, whether predator, prey, or decomposer, plays a unique role. A diverse ecosystem is more resilient to changes, such as climate fluctuations or human activities, because it can adapt more effectively. Protecting the food chain means preserving biodiversity, which in turn supports ecosystem stability.
Human Impact and Conservation
Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and overfishing, can disrupt food chains. These disruptions often have cascading effects, leading to the decline of species and the degradation of ecosystems. Understanding the importance of the food chain underscores the need for conservation efforts, including habitat protection and sustainable practices, to maintain ecological balance.







